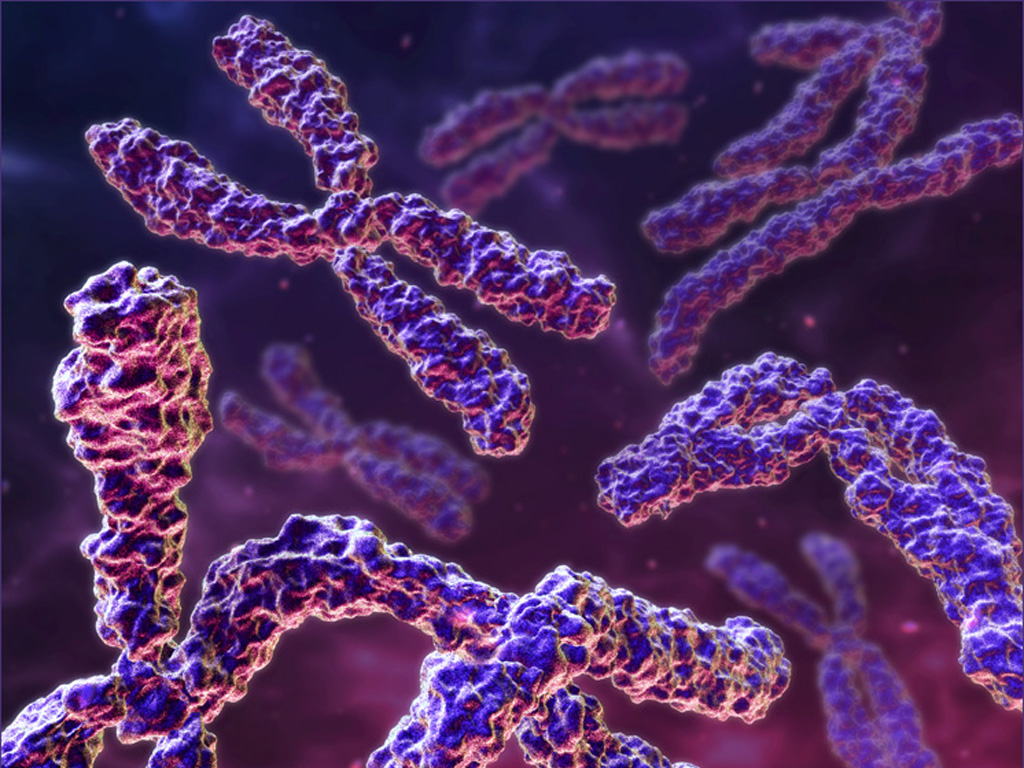
vocabulary
•Nucleus: 细胞核; Nucleolus: 核仁; Nucleoid: 类核
• Mitosis: 有丝分裂; Meiosis: 减数分裂
Interphase: 分裂间期; Prophase: 分裂前期; Metaphase: 分裂中期; Anaphase: 分裂后期; Telophase: 分裂末期
• Histone: 组蛋白
• Nucleosome: 核小体
•Chromosome: 染色体; Chromatin: 染色质; eu- 真染色质; hetero- 异染色质
• Centromere: 中心粒; Telomere: 端粒
====================================================
- WHAT is chromosome:
Structure containing the genes of a cell and made of a single DNA molecule and its associated proteins.
- HOW long is DNA in an chromosome

HOW LONG IS DNA, shown by prof. Dong.
→A chromosome is too long to fit into a cell without compaction.
- WHY is DNA packed into chromosomes
- Chromosome is a compact form of the DNA that readily fits inside the cell
- To protect DNA from damage
- DNA in a chromosome can be transmitted efficiently to both daughter cells during cell division
- Chromosome confers an overall organization to each molecule of DNA, which regulates gene expression as well as recombination
——————————————————————————
Diversity of chromosomes
in terms of:
- Shape: circular or linear
- Number: species-specific
eg. -fruitfly 8; -human 46; -horse 64; -dog 78; -chicken 78
-maize 20; -rice 24; -wheat 42
- Copy number: haploid单倍体, diploid双倍体, polyploid 多倍体
- Overall structure: highly different between prokaryotes 原核生物and eukaryotes真核生物
——————————————————————————-
Next section we will first talk about prokaryotic chromosome structure of DNA.